Your BMI is 39
According to your BMI, you are obese. Your BMI is falling very close to the extremely obese category. This alone should be enough to motivate you to lose weight. Dieting and exercising alone might not bring the desired results and if that is the case, consult your doctor about available weight loss surgeries.
Each person’s body is unique and may have different caloric needs. When your body’s caloric balance status is in caloric excess, it means that you are eating more calories than your body is using and you will store these excess calories as fat. Besides diet and behavior, the environment and genetic factors may also have a significant effect in causing people to be overweight or obese. It is important to understand the risks you are facing if you do not take any measures to lose weight.
Overweight and obese individuals are at increased risk for many diseases and health conditions, including the following:
If you are seriously overweight, have tried dieting and exercise but you fail to lose weight, weight loss surgery is a viable option to consider. If your weight is impacting the quality of your life, bariatric surgery can help you regain control of your life and improve your health.
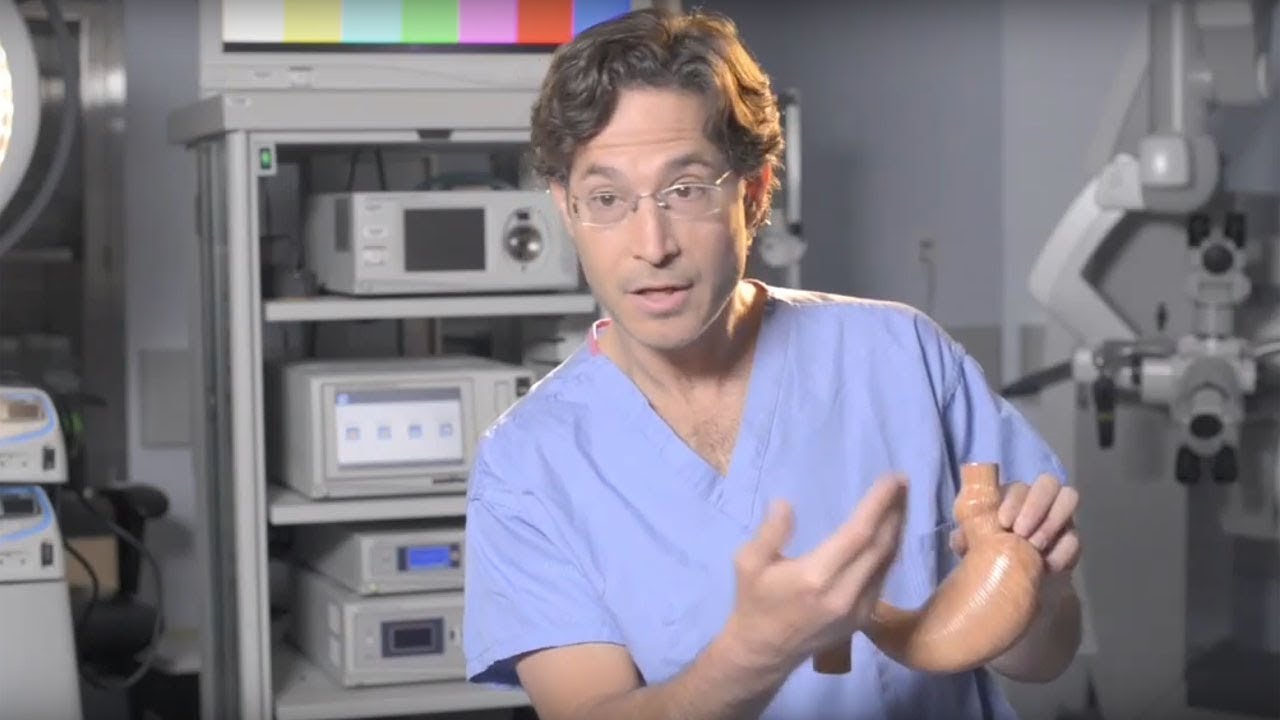
Lap Band Procedure for a BMI 39
The lap band procedure is recommended for BMI over 35, it can also be done for obese patients whose BMI is lower than 35. This surgically implanted device helps adults lose considerable weight by limiting the stomach’s capacity, thus giving the patient the feeling of being full. If you require a weight loss surgery procedure there’s no need to worry about the expenses, most of them will be covered by insurance, just check the terms of your insurance policy.
The narrowed opening between the stomach pouch and the rest of the stomach can be adjusted by inflating (adding saline fluid) or deflating the band (removing saline fluid). For obese patients who have failed to lose weight through non-surgical methods, the lap band is a recommended surgical option.
Gastric Bypass Procedure for a BMI 39
Gastric bypass helps you lose weight by changing how your stomach and small intestine handle the food you eat. It is performed in 2 steps: making your stomach smaller by dividing it into a smaller upper section and a larger bottom section, and the bypass. Doctors often use the BMI and health conditions, such as type 2 diabetes and high blood pressure to determine who is a candidate for weight loss surgery.
Gastric bypass is done for patients who have a BMI over 40, but can also be recommended for obese patients with a BMI of 35. You may lose half or more of your extra weight in the first 2 years and most people lose about 10-20 pounds each month in the first year after surgery.
Gastric Sleeve Procedure for a BMI 39
Gastric sleeve surgery, or sleeve gastrectomy, is a restrictive bariatric operation designed to make the stomach smaller, in order to help obese people lose weight and regain control of their life. Lifelong changes need to be done after this procedure in order to maintain your weight. If your BMI is between 30 and 40, you may be a candidate for gastric sleeve surgery.
During this procedure, more than half of your stomach is removed, leaving only a thin vertical sleeve about the size of a banana. This is not a reversible procedure! Your doctor will give you specific instructions before and after the surgery. Even if you had surgery, you will still need to have a healthy diet and get regular exercise, in order to reach your weight goal and avoid regaining weight.
Once you have the permission of your doctor regarding physical activity, design a daily routine that takes into account your current level of fitness. Frequency is more important than intensity. Start out with 10-15 minutes performed daily and move on 15-20 after two or three weeks, when exercising becomes so normal, that your body starts asking for it.
Once your body is ready for sessions of 40-50 minutes every day, you are set for effective weight loss. To avoid boredom, alternate cardio exercises (running, rope jumping, biking, hiking) with strength training exercises (weight lifting, squats, pull-ups, etc.) and stretching exercises (yoga, Pilates, etc.) for a whole body workout.